Source: Ericsson, 2009
The following are the key functional nodes/network elements in the LTE architecture:
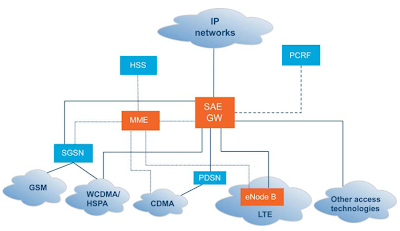
Evolved Node B (eNB)
- eNodeB is the entity that supports air interface and performs radio resource management
- Provides radio resource management functions such as IP header compression, user data encryption, and routing the user date to the Serving Gateway
- The radio interface provided by eNodeB can be shared by several operators by having separate MME, SGW & PDN Gateway.
- It serves as the mobility anchor for the user plane.
- It takes care of inter-eNodeB handovers & User Equipment (UE) mobility between 3GPP networks.
- It is responsible for routing/forwarding data packets between the eNodeB & PDN Gateway
- It provides the UE with connectivity to the external packet data networks such as Internet.
- It serves as the anchor point for intra-3GPP network mobility, as well as mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP networks.
- It takes care of Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF), which includes Quality of Service (QoS), online/offline flow-based charging data generation, deep-packet inspection, and lawful intercept.
- It manages mobility, UE identities and security parameters
- It operates in the Control plane and provides functions such as managing session states, authentication, mobility with 3GPP 2G/3G nodes, and roaming.







I’ve recently started a blog, the information you provide on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
ReplyDeleteits good stuff.. didnt have a clue on LTE but in a few minutes.. am getting to grips with the content.Thanks alot.
ReplyDelete