Alca-Lu claims to have done industry’s first live field tests of Coordinated Multipoint Transmission (CoMP) a new technology that will increase data transmission rates and help ensure consistent service quality and throughput on Long Term Evolution (LTE) wireless broadband networks as well as on 3G networks. The underlying technology coordinates and combines signals from multiple antennas, CoMP, will make it possible for mobile users to enjoy consistent performance and quality when they access high-bandwidth services whether they are close to the center of an LTE cell or at its outer edges.
Alca-Lu didn't publish any performance numbers and didn't quantify the performance improvement. The press release states that the testing was done using the modem and controller elements of Alca-Lu's LTE base station (eNodeB).
For more information, read the press release.
▼
Monday, October 19, 2009
Saturday, October 17, 2009
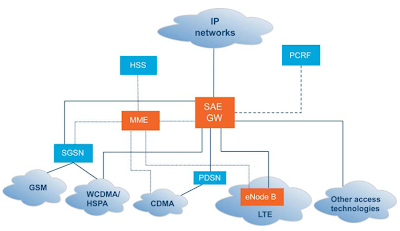
LTE network architecture and functional nodes/elements
Source: Ericsson, 2009
The following are the key functional nodes/network elements in the LTE architecture:
Evolved Node B (eNB)
- eNodeB is the entity that supports air interface and performs radio resource management
- Provides radio resource management functions such as IP header compression, user data encryption, and routing the user date to the Serving Gateway
- The radio interface provided by eNodeB can be shared by several operators by having separate MME, SGW & PDN Gateway.
- It serves as the mobility anchor for the user plane.
- It takes care of inter-eNodeB handovers & User Equipment (UE) mobility between 3GPP networks.
- It is responsible for routing/forwarding data packets between the eNodeB & PDN Gateway
- It provides the UE with connectivity to the external packet data networks such as Internet.
- It serves as the anchor point for intra-3GPP network mobility, as well as mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP networks.
- It takes care of Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF), which includes Quality of Service (QoS), online/offline flow-based charging data generation, deep-packet inspection, and lawful intercept.
- It manages mobility, UE identities and security parameters
- It operates in the Control plane and provides functions such as managing session states, authentication, mobility with 3GPP 2G/3G nodes, and roaming.
Friday, October 16, 2009
An Introduction to Long Term Evolution (LTE)
Are you looking for a Long Term Evolution (LTE) powerpoint presentation to bring you/your team up to speed on the basics? This powerpoint presentation would help you jump start on the LTE technology. You can treat this as a LTE 101 course. The PPT material is organized as per the following topics.
Download PDF
What is LTE?
Advantages of LTE
Comparison of LTE speed
LTE Radio Technologies
LTE Architecture
Functional LTE network elements
Major LTE vendors
LTE – Early Adopters
A glance at LTE Market
Download PDF
What is LTE?
Advantages of LTE
Comparison of LTE speed
LTE Radio Technologies
LTE Architecture
Functional LTE network elements
Major LTE vendors
LTE – Early Adopters
A glance at LTE Market
10 things you should know about LTE
LTE has become the buzz word in the next generation data networks. There has been lots of talks about how LTE can improve the speed of mobile broadband networks, with a magic wand. There are several vendors in this market space trying to divide the pie. Do you want to learn more about LTE? This FAQ should help you understand the basics of LTE. You can treat this as LTE 101s.
1) What does LTE stand for?
1) What does LTE stand for?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution
2) What is LTE?
LTE is a mobile broadband technology promising higher data transfer rates. It defines a new radio access technology that is optimized for IP-based traffic.
It has enhancements to the UMTS 3G technology to provide significantly faster data transfer rates.
3) Which "radio" technologies does LTE use?
LTE will utilize Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for downlink and Single Carrier - Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) for uplink. SC-FDMA uses a constant power which enables high RF power amplifier efficiency in the mobile handset devices. This significantly lowers the power consumed from your handset's battery, thereby letting you to browse Internet for a longer time :)
4) How much speed (i.e., data transfer rates) can I get with LTE ?
LTE offers download speeds of at least 100 Mbps, and upload speed of at least 50 Mbit/s
5) Is LTE, the 4G technology?
Though LTE is "marketed" as 4G, LTE in its current form, is not the REAL 4G technology. A simple reason being the 4G technology requires 1Gbps data download speed and LTE cannot provide it today.
(Also, read Comparison of download speeds - 2G, 3G, LTE & 4G)
6) What is LTE-A?
LTE-A stands for Long Term Evolution Advanced. It is developed with the objective of meeting 4G requirements.
7) What is the 3GPP specification that describes LTE?
3GPP Release 8
8) Who are some of the LTE network equipment vendors?
All major telecom equipment providers such as Ericsson, AlcaLu, Motorola, Nokia have LTE network equipment
9) What are some advantages to end users provided by LTE?
- Faster data downloads/uploads
- Improved response for applications and hence, improved end-user experience
10) What are some advantages to network operators, provided by LTE?
LTE adoption gives network operators the following benefits:
- High network throughput
- Low latency
- Plug and Play architecture
- Low operating costs
- All-IP, packet based network
- Simplified upgrade path from 3G networks
What is the speed of LTE networks?
How much speed does Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks offer? How does it compare against the speed or data rates offered by other mobile broadband technologies such as 2G, 2.5G, 3G. What is the data rate promised by 4G networks? The following chart should put the data rates of different mobile broadband technologies in perspective (Note: The numbers are theoretical maximums provided by the specifications)
Let us take for example, you want to download a 1 MB movie file using your mobile broadband Internet. Using 2G technology, it takes you 10 minutes, to download a single 1 MB movie file. Using 2.5G technology, you can download nearly 30 such movie files in 10 minutes. Using 3G technology, you can download, 1000 such movie files in 10 minutes. LTE technology would allow you to download 8000 movie files in 10 minutes.
Tuesday, October 13, 2009
Cisco acquires LTE solutions provider Starent networks
Cisco today announced a definitive agreement to acquire the Long Term Evolution (LTE)/ Evolved Packet Core (EPC) solutions vendor Starent networks. Starent’s platforms can serve as the Mobility Management Entity (MME), Serving Gateway (SGW), Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW), and Evolved Packet Data Gateway (ePDG). Starent won the Verizon deal last year, competing against Ericsson. Starent has foot in UMTS, WiMax, WiFi, & Femto Cell technologies too. It is very clear that the products and technologies of Starent are going to complement Cisco's networking gear. Considering Starent's size of 1000 employees, it is going to be very easy for Cisco to absorb them. This is Cisco's second acquisition in a week. Last week, Cisco announced that it is going to acquire video infrastructure provider Tandberg for $3 billion.
Also read:
Acquisition of Starent Networks Expands Cisco's Mobile Internet Offerings for Service Providers
Also read: